Determination of Multiple Elements in Food 2 - National Food Safety Standard
Publish Date: 2016-12-23
Implement Date: 2017-06-23
Issued by: The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China, and the State Food and Drug Administration
Standard Status: currently valid
This is the National Standard of the People's Republic of China, GB5009-268-2016, Determination of Multiple Elements in Food, there are two analytical methods. Method 1: Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS). Method 2: Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES). This article describes the Method 2.
The Method 2 of this standard specifies Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) for the determination of multiple elements in food. Suitable for determination of aluminum, boron, barium, calcium, copper, iron, potassium, magnesium, manganese, sodium, nickel, phosphorus, strontium, titanium, vanadium and zinc in food.
The English version of this standard is translated from the Chinese original GB5009-268-2016. In case of discrepancies in the translated version, the original Chinese standard GB5009-268-2016 (Chinese version) shall prevail. This translated version can provide reference for food production enterprises.
Standard Text of GB5009-268-2016
A. Standard Cover of GB5009-268-2016
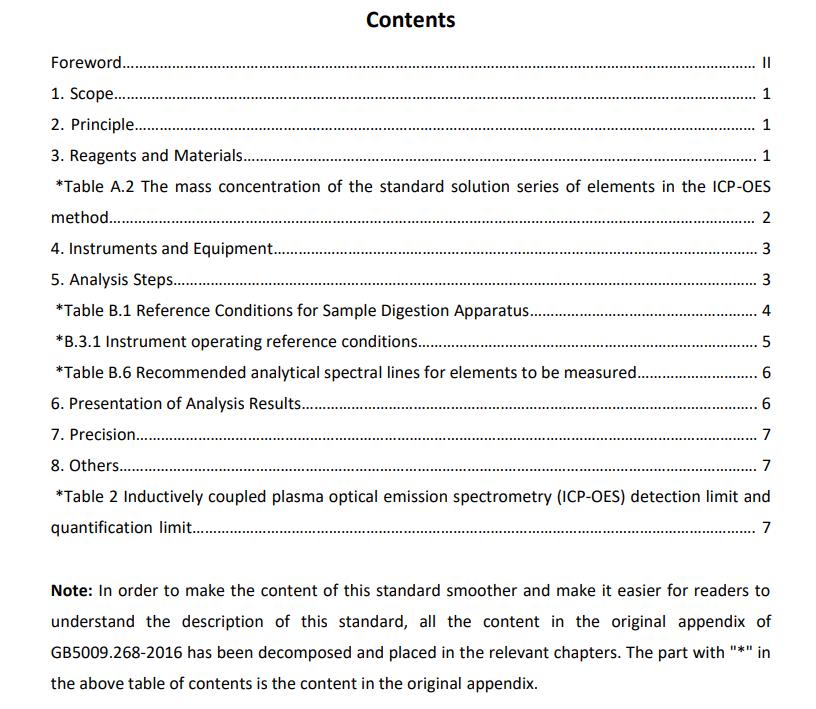
 B. Table of Contents
B. Table of Contents
 C. Standard Preface of GB5009-268-2016
C. Standard Preface of GB5009-268-2016
Foreword
This standard replaces:
* The second method of GB5413.21-2010 "National Food Safety Standard, Determination of Calcium, Iron, Zinc, Sodium, Potassium, Magnesium, Copper and Manganese in Infant and Young Children's Food and Dairy";
* GB/T23545-2009 Determination of Manganese in "Liquor", Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry";
* GB/T23374-2009 "Determination of Aluminum in Food, Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry";
* GB/T18923.11-2002 "Determination method of Potassium, Phosphorus, Iron, Calcium, Zinc, Aluminum, Sodium, Magnesium, Boron, Manganese, Copper, Barium, Titanium, Vanadium, Nickel, Cobalt and Chromium Content in Honey, Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry (ICP-AES);
* The second method of SN/T0856-2011 "Testing Methods for Tin in Canned food for Import and Export";
* SN/T2208-2008 "Determination of Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminum, Calcium, Chromium, Iron, Nickel, Copper, Zinc, Arsenic, Strontium, Molybdenum, Cadmium, Lead, Mercury and Selenium in Aquatic Products, Microwave Digestion-Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry";
* SN/T2056-2008 "Determination of lead, arsenic, cadmium, copper and iron content in imported and exported tea, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry";
* SN/T2049-2008 "Determination of copper, nickel, lead, manganese, cadmium and titanium in import and export food grade phosphoric acid, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry";
* SN/T2207-2008 "Determination of Arsenic, Calcium and Lead Content in Imported and Exported Food Additives DL-Tartaric Acid, Inductively Coupled Plasma Atomic Emission Spectrometry";
* NY/T1653-2008 "Determination of Mineral Elements in Vegetables, Fruits and Products, Inductively Coupled Plasma Emission Spectroscopy".
Compared with the second method of GB5413.21-2010, the main changes of this standard are as follows:
—— The name of the standard was changed to "National Food Safety Standard - Determination of Multiple Elements in Food";
—— Added inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry as the first method;
—— Modify inductively coupled plasma emission spectrometry as the second method;
—— Modified the scope of application;
—— Modified some contents of sample preparation;
—— Modified the content of sample digestion;
—— Increased method detection limit and quantification limit.
D. Norma Content of GB5009-268-2016
National Food Safety Standard
Determination of Multiple Elements in Food
1. Scope
This standard specifies inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) for the determination of multiple elements in food.
The first method is suitable for the determination of boron, sodium, magnesium, aluminum, potassium, calcium, titanium, vanadium, chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, nickel, copper, zinc, arsenic, selenium, strontium, molybdenum, cadmium, tin, antimony, barium, mercury, thallium and lead in food. The second method is applicable to the determination of aluminum, boron, barium, calcium, copper, iron, potassium, magnesium, manganese, sodium, nickel, phosphorus, strontium, titanium, vanadium and zinc in food.
The Method 2: Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy
(ICP-OES)
2. Principle
After the sample is digested, it is measured by an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometer, and qualitatively determined by the wavelength of the characteristic spectral line of the element; the intensity of the spectral line signal of the element to be detected is proportional to the element concentration for quantitative analysis.
3. Reagents and Materials
Unless otherwise stated, all reagents used in this method are of guaranteed reagent (Gr). The water is the first grade water specified in GB/T 6682.
3.1 Reagents
3.1.1 Nitric acid (HNO3): Guaranteed reagent (Gr) or higher purity.
…….
3.2 Reagent Preparation
3.2.1 Nitric acid solution (5+95): Take 50 mL of nitric acid, slowly add it to 950 mL of water …….
…….
3.3 Standard Chemicals
3.3.1 Elemental stock solution (1000mg/L or 100mg/L): potassium, sodium, calcium…….
…….
4. Instruments and Equipment
4.1 Inductively coupled plasma - optical emission spectrometer
4.2 Balance: Sensitive amount is 0.1mg and 1mg.
4.3 Microwave digestion apparatus: Equipped with PTFE digestion inner tank.
4.4 Pressure digestion tank: Equipped with PTFE digestion inner tank.
4.5 Constant temperature drying oven
4.6 Adjustable temperature control electric heating plate.
4.7 Muffle furnace
4.8 Adjustable temperature-controlled electric heating furnace
4.9 Sample crushing equipment: homogenizer, high-speed crusher
5. Analysis steps
5.1 Specimen Preparation
5.1.1 Solid samples
5.1.1.1 Dry samples
For samples with low water content such as beans, grains …….
…….
5.1.2 Liquid samples
Samples of soft drinks, condiments, etc., shake well.
5.1.3 Semi-solid samples
Stir well.
5.2 Sample digestion
Note: …….
5.2.1 Microwave digestion
Weigh 0.2g~0.5g of solid sample (accurate to 0.001g, the sample with more water content can be appropriately increased to 1g) or …….
Table B.1 Reference Conditions for Sample Digestion Apparatus
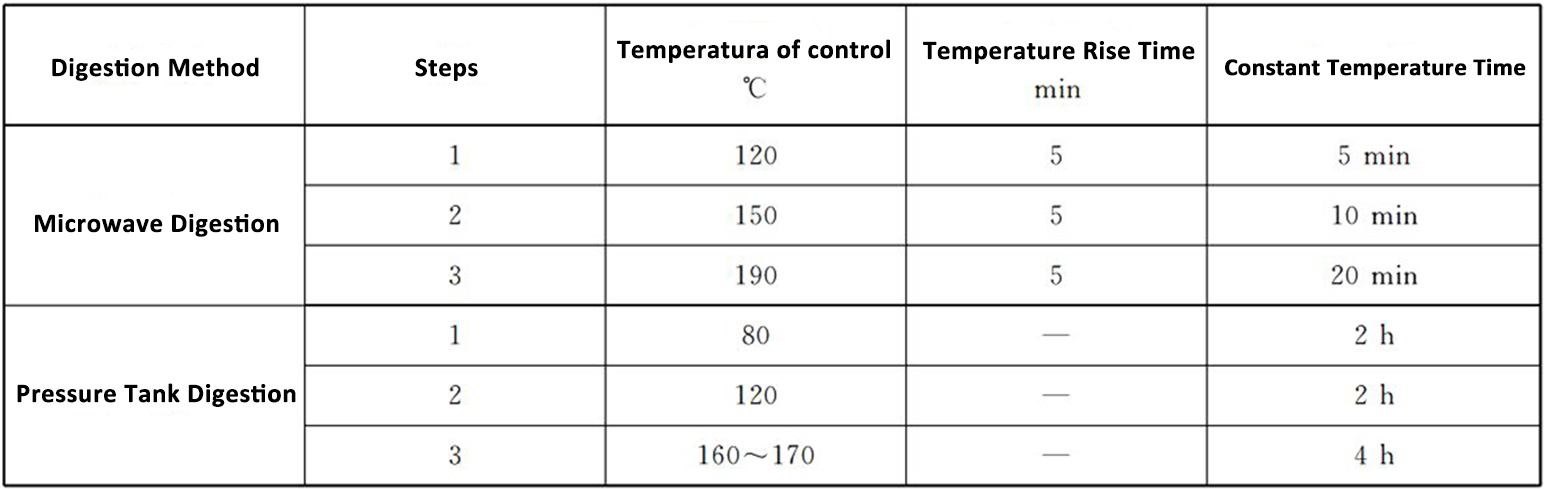 5.2.2 Pressure tank digestion method
5.2.2 Pressure tank digestion method
Weigh 0.2g ~ 1g of solid dry sample…….
5.2.3 Wet digestion method
Accurately weigh 0.5g ~ 5g (accurate to 0.001g) or…….
5.2.4 Dry Digestion Method
Accurately weigh 1 g to 5 g (accurate to 0.01 g) or accurately pipette…….
5.3 Instrument reference conditions
Optimize the operating conditions of the instrument so that the sensitivity and other indicators of the element to be measured meet the analysis requirements. Edit the determination method and select the appropriate analytical spectral line for each element to be measured. Refer to B.3.1 for the operating reference conditions of the instrument, and see Table B.6 for the recommended analytical spectrum of the element to be measured.
…….
5.4 Preparation of standard curve
Inject the series working solutions of standard into the inductively coupled plasma - optical emission spectrometer. Determine the intensity signal response value of the analytical spectral line of the element to be tested. Take the concentration of the element to be tested as the abscissa and the response value of its analytical spectral line intensity as the ordinate, draw a standard curve.
5.5 Determination of sample solution
…….
6 Presentation of analysis results
The content of the element to be tested in the sample is calculated according to formula (3):
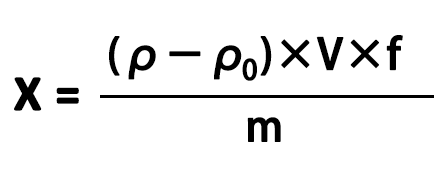 --------------- (3)
--------------- (3)
In formula (3):
X ---- The content of the element to be measured in the sample, in milligrams per kilogram or milligrams per liter (mg/kg or mg/L);
…….
7. Precision
When the content of each element …….
8 Others
The solid sample is calculated from a constant volume of 0.5 g to 50mL. Liquid samples are calculated from a constant volume of 2 mL to 50mL. The detection limit and quantification limit of each element in this method are shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) detection limit and quantification limit
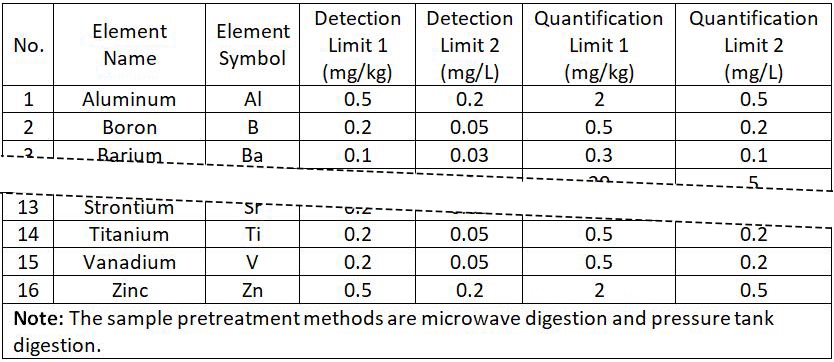
______________________________________
Note: Commonly used Chinese food standards include mandatory national standards (the code starts with "GB") and recommended national standards (the code starts with "GB/T")
If you need other Chinese standards related to food, please "Contact Us". We do our best to find and provide translation services.
--------------------------------------------------------------
To obtain the text of this standard (English version), a payment of 60 US dollars ($60) is required. Payment can also be made in RMB, Euro, British pound, Australian dollar, New Zealand dollar, Canadian dollar, Thai baht, Swiss franc, and ruble. Payment can be made by Visa, UnionPay, credit card, debit card, wire transfer, Paypal, Alipay and WeChat. After payment, please tell us your payment name, country and location where payment is made, payment time, and email address for receiving documents in "Contact Us". If you still haven't received the document after 1 day after payment, please "contact us" so that we can solve it in time. When the document is received, please reply "Document received". If there is no response within 10 days, we consider the document to have been received. You can also ask for help through "Contact Us".
--------------------------------------------------------------
References Articles
1. Principle of Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS)
2. Principle of Inductively Coupled Plasma - Optical Emission Spectrometer
3. Determination of Tin in Food 1 - National Food Safety Standard
4. Determination of Tin in Food 2 - National Food Safety Standard
5. Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System - General Requirements for Food Processing Plant
6. General Hygienic Regulation for Food Production - National Food Safety Standard
7. GB5749—2022 Standards for Drinking Water Quality
--------------------------------------------------------------
Related Testing Equipment
1. SUP-70 Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer ( ICP-MS): can detect dozens of elements and isotopes at one time, ultra-trace analysis, automatic.
2. SUP-70M Vehicle-mounted Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer: can detect dozens of elements and isotopes in one-time ultra-trace, anti-vibration.
3. SUP-72 Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer: is a high-sensitivity, rapid food detection and ultra-trace analysis instrument, automatic.
4. SUP-735 Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometer ( ICP-MS /MS, ICP-QQQ ): is a space tandem multi-stage quadrupole mass spectrometer equipped with an inductively coupled plasma.
5. Laboratory Equipment and Instruments: include precision weighing equipment, evaporators, drying ovens and food testing instruments.
--------------------------------------------------------------



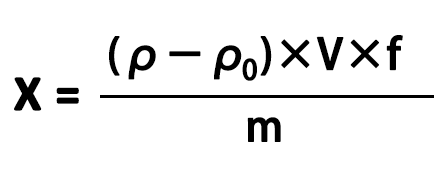 --------------- (3)
--------------- (3)