Standards for Drinking Water Quality, GB5749-2006
Standard Number: GB5749-2006
Publish Date: 2006-12-29
Implement Date: 2007-07-01
Issued by: the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China and the National Standardization Administration
Standard Status: currently valid
This is GB5749-2006, Standards for Drinking Water Quality, a food quality standard of the People's Republic of China. It is issued by the Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China and the National Standardization Administration.
The English version of this standard is translated from the Chinese original GB5749-2006. In case of discrepancies in the translated version, the original Chinese standard GB5749-2006 (Chinese version) shall prevail. This translated version can provide reference for food production enterprises.
Standard Text of GB5749-2006
A. Standard Cover of GB5749-2006
 B. Table of contents
B. Table of contents

C. Standard Preface of GB5749-2006
Foreword
All technical contents of this standard are mandatory.
This standard replaces “GB 5749-1985 Standards for Drinking Water Quality” since the date of implementation.
Compared with GB 5749-1985, the main changes of this standard are as follows:
― The number of water quality indicators was added from 35 in GB 5749-1985 to 106, with an increase of 71; 8 were revised; amongthem:
a) Microbial indicators increased from 2 to 6, and escherichia coli, heat-resistant coliform bacteria, giardia and cryptosporidium were added; total coliform bacteria isrevised;
b) Drinking water disinfectants increased from 1 to 4, and monochloramine, ozone and chlorinedioxide were added;
c) Inorganic compounds in toxicology index increased from 10 to 21 items, with bromate, chlorite, chlorate, antimony, barium, beryllium, boron, molybdenum, nickel, thallium and cyanogen chloride been added; Arsenic, cadmium, lead and nitrate were revised;
Organic compounds in toxicology index increased from 5 to 53, adding formaldehyde, trihalomethane, methylene chloride, 1,2-dichloroethane, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, bromoform, chlorodibromomethane, bromodichloromethane, epoxy chloropropane, vinyl chloride, 1,1-dichloroethylene, 1,2-dichloroethylene, trichloroethylene, tetrachloroethylene, hexachlorobutadiene, dichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetic acid, trichloroacetaldehyde, benzene, toluene, xylene, ethylbenzene, styrene, 2,4,6-trichlorophenol, chlorobenzene, 1,2- dichlorobenzene, 1,4 - dichlorobenzene, trichlorobenzene, Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, acrylamide, micro capsule algal toxins-LR, bentazone, chlorothalonil, deltamethrin, dimethoate, 2,4-D, heptachlor, hexachlorobenzene, lindane, malathion, parathion, methyl parathion, pentachlorophenol, atrazine, carbofuran, chlorpyrifos, dichlorvos, glyphosate; carbon tetrachloride was revised;
d) Sensory properties and the general chemical index increased from 15 to 20 items, with oxygen consumption, ammonia nitrogen, sulfur, sodium and aluminum been added; turbidity wasrevised;
e) The total alpha radioactive indicator in radioactive indicators was revised.
― The water source selection and water health protectionparts were deleted.
― Simplified water quality detection regulations of water supply departments; part of the contents has been listed in the Hygienic Standard for the Drinking Water Centralized SupplyUnit.
― Add Appendix A.
― Add References.
The appendix A of this standard is an informative one.
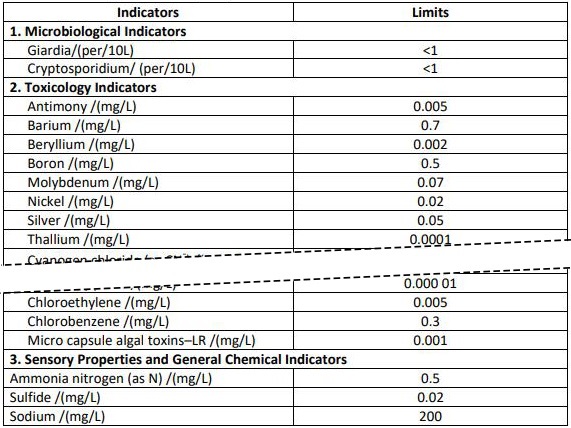
The implementation and the date of the indicators in Table 3 Non-regular Water Quality Index and Limit of this standard are stipulated by the provincial governments according to the local actual situation, which should be submitted to the Standardization Administration of China, the Ministry of Construction and the Ministry of Health for record. Since 2008, the three departments above will report the implementation situation of non-regular water quality indices of each province and all indices will be implemented by July 1, 2012 at the latest.
This standard is proposed by the Ministry of Health, the Ministry of Construction, Ministry of Water Resources, the ministry of land and resources and State Environmental Protection Administration, etc. This standard is centralized by the ministry of health of the People's Republic of China.
The standard is drafted by the Institute of Environmental Health and Product Safety Related, China CDC.
The units which participated in the drafting of this standard are: Health Supervision of Guangdong province, Health Supervision of Zhejiang province, Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Shanghai Center for Disease Control and Prevention, China Urban Water Supply and Drainage Association, China Water Resources and Hydropower Research Institute, and Environmental Standards Institute of the State Environmental Protection Administration.
Main drafters of this standard: Yinlong Jin, Xueli E, Changjie Chen, Xi-ping Chen, Lan Zhang, Yayan Chen, Zugen Cai, Rihua Gan, Hang Shentu, Changyi Guo, Jianrong Wei, Ruizhu Ning, Wenzhao Liu, Linlin Hu.
Participant drafters of this standard: Shiwen Cai, Shaobin Lin, Fan Liu, Xiaoyuan Yao, Kunming Lu, Guoguang Chen, Huaidong Zhou, Yanping Li.
This standard was firstly published in August, 1985 and this is the first revision.
D. Total Pages: 14, (including cover, preface, contents, table of contents, tables, and images of GB5749-2006).
Total Words: 2563, (Table of contents, tables, and images cannot count the words)
E. Standard Content of GB5749-2006
Standards for Drinking Water Quality
1. Scope
The sanitary requirements of the drinking water and its source, centralized water supply unit, secondary water supply and health security products related to drinking water as well as water quality monitoring and testing methods.
This standard applies to drinking water from all kinds of centralized water supply in urban and rural areas, and also applies to decentralized drinking water supply.
2. Normative Documents Cited From Standards
The clauses of the documents mentioned below become clauses of this standard through being cited by this standard. For all documents cited with dates, all modifications (with the exception of error corrections) or modifications are not applicable for this standard, but all parties who conclude the agreement on the basis of this standard are still encouraged to study the possibility of whether or not to adopt the new versions of the aforementioned documents. Documents without dates and their new versions are applicable for this standard.
……
4. Hygiene Requirements for Drinking Water
……
4.1.6 The drinking water quality shall meet the hygienic requirements in table 1 and table 3. The disinfectant limit of drinking water from centralized water supply factory and the disinfectant residue in the finished water and the tap water of pipe network shall meet the requirements in Table 2.
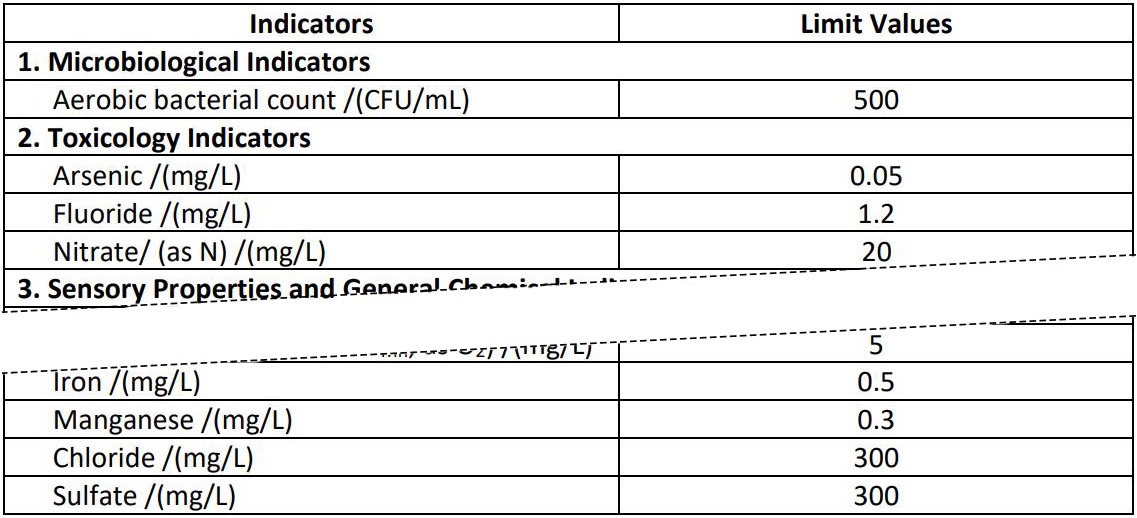
4.1.7 Due to some restrictions, some quality indices of water from small centralized and decentralized water supply should be temporarily implemented in accordance with Table 4. While the rest of the index should still refer to Table 1, 2 and 3.
4.1.8 In the event of unexpected public events impacting water quality, sensory properties and general chemical indicators can be eased appropriately with the approval of the municipal people's government at or above.
4.1.9 When drinking water contains the indicators listed in Table A.1 in Appendix A, the limit in this table can be referred to for evaluation.
Table 1 – General Water Quality Indicators and Limits
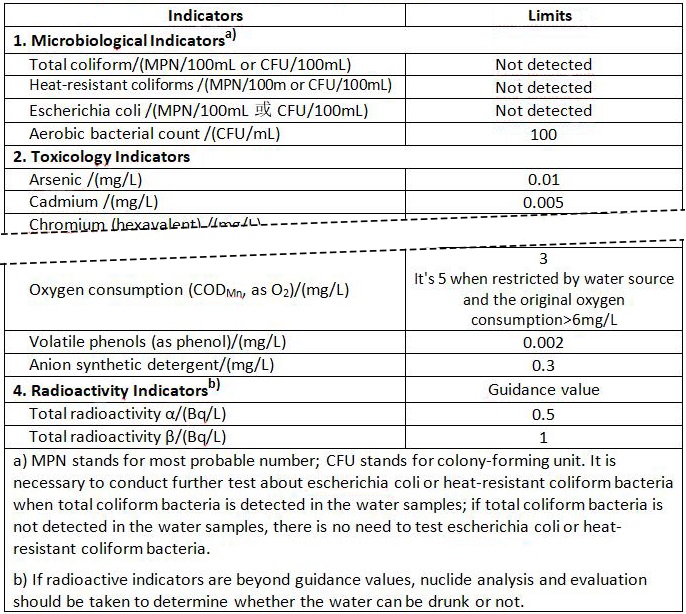
Table 2 - Regular Indicators and Requirements of Drinking Water Disinfectant
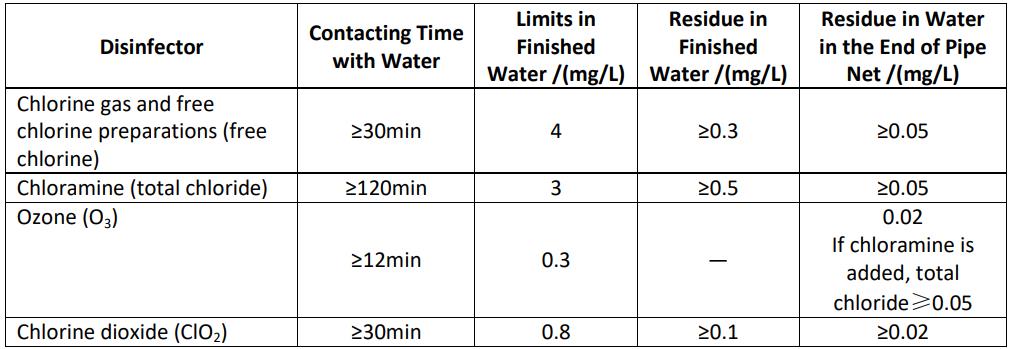
Table 3 - Non-regular Water Quality Indicators and Limit Values
……
Table 4 - Partial Water Quality Indicators and Limits of Small Centralized and Decentralized Water Supply
……
Appendix A
Table A.1 Drinking Water Quality Reference Indices and Limits
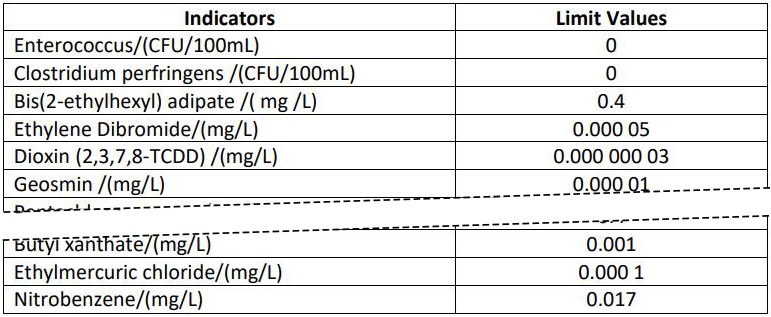
……
________________________
Note: Commonly used Chinese food standards include mandatory national standards (the code starts with "GB") and recommended national standards (the code starts with "GB/T")
If you need other Chinese standards related to food, please "Contact Us". We do our best to find and provide translation services.
----------------------------------------------------
To obtain the text of this standard (English version), a payment of 50 US dollars ($50) is required. Payment can also be made in RMB, Euro, British pound, Australian dollar, New Zealand dollar, Canadian dollar, Thai baht, Swiss franc, and ruble. Payment can be made by Visa, UnionPay, credit card, debit card, wire transfer, Paypal, Alipay and WeChat. After payment, please tell us your payment name, country and location where payment is made, payment time, and email address for receiving documents in "Contact Us". If you still haven't received the document after 1 day after payment, please "contact us" so that we can solve it in time. When the document is received, please reply "Document received". If there is no response within 10 days, we consider the document to have been received. You can also ask for help through "Contact Us".
----------------------------------------------------
References Articles
1. GB5749—2022 Standards for Drinking Water Quality
2. GB17323-1998 Bottled Purified Water for Drinking
3. GB19298-2014 Packaged Water for Drinking
4. GB8537-2018 Drinking Natural Mineral Water
5. GB/T6682-2008 Water for Analytical Laboratory Use - Specifications and Test Methods
6. GB14881-2013 General Hygienic Regulation for Food Production
7. GBT/27341-2009 Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System - General Requirements for Food Processing Plant
8. GB5009-268 Determination of Multiple Elements in Food 1
9. GB5009.16-2014 Determination of Tin in Food 1 - National Food Safety Standard
----------------------------------------------------
Related Equipment
1. River and Lake Drinking Water Purification Treatment Equipment: can treat raw water of rivers and lakes into drinking water, is ideal drinking water purification treatment equipment for a water plant.
2. Well and Mountain Water Purification Treatment Equipment for Drinking: The water purification treatment equipment can treat raw water of well and mountain into drinking water, have no RO equipment, automatic backwashing, and large processing capacity.
3. Food Safety Testing and Inspection instruments Equipment: are used for inspection of pesticide residues, heavy metals.
4. Microbiology Testing Equipment and Instruments: include incubators, gadgets, and instruments, are one of the food safety testing equipment.
5. Laboratory Equipment and Instruments: include precision weighing equipment, evaporators, drying ovens and food testing instruments.
6. Food Production Monitors and Online Detectors: are capable of detecting and monitoring the quality of each product on the food production line, is important testing equipment.
---------------------------------------------------- 





